Why Use Plastic Pipe Systems?
Plastic was invented because of human’s desire for making a better life for themselves. Scientific curiosity was sparked by plastic. While plastics have had their share of ups and downs, there are definitely some advantages of plastic pipes.
Plastic pipe systems have a wide variety of service requirements that they can fulfill. The European Product standards correctly define the requirements for each application along with their specific characteristics.
Hygienic requirements – conveyance of drinking water
Safety requirements – conveyance of gas
Temperature resistance over decades – plastic pipes for radiating heating and floor heating
High Chemical resistance – sewer applications
The benefits of plastic pipes include being perfectly able to fulfill the specific requirement, with a high level of performance over a long lifetime and with reliability and safety. Success is achieved due consistently maintaining a high quality level. Two factors that are important for the performance of the pipes over a long period of time are reliability and safety.
Advantages Of Using Plastic Pipes

The pipes are always classified by their ring stiffness. The ring stiffness of pipes is important if they are needed to withstand external loading during installation. The flexible nature of pipes ensures that they would not fail. The deflection can take place while keeping up with its original function, without breaking.

For over 50 years, plastic pipes have served us successfully. The predicted lifespan of a plastic pipe is over 100 years! Plastic pipes have always been classified on the basis of long-term pressure testing.

The use of plastic pipes also takes into account, the safety factor. The qualified nominal pressure of a plastic pipe has always included a safety factor. This helps in the design of the piping system.
Fast Guide To Materials
Various types of plastics are used in plastic piping systems. These plastic materials have a wide range of properties to display which makes plastic pipes the ideal choice for anything, from pressurized water mains to gravity sewer systems and indoor heating systems. The four main types of materials used in plastic pipes are: PVC, PE, PEX and PP. A variety of pipe systems have these materials. Industrial pipe systems are mainly found in ABS.

Polyvinyl Chloride or PVC is a thermoplastic material derived from common salt and fossil fuels. The first PVC pipes dates back to 1930s. In the 1950s, these were used to bring in fresh drinking water to the growing urban population. This material has made a significant contribution to public health, hygiene and well-being.

Derived from fossil fuels, Polyethylene or PE is a tough thermoplastic material. It is used for a broad range of pressure applications which include transportation of drinking water and natural gas, irrigation, sewers, and drainage lines.

Made from polypropylene, PP is a thermoplastic polymer. Though invented in the 1950s, it has been used only since 1970s. The high impact resistance, with good stiffness and excellent chemical resistance, make this material suitable for sewer applications. This material is used for in-house discharge systems for soil and waste when it’s continuous, and also for warm water supply when it’s short-term.

PEX is commonly referred to as cross-linked polyethylene. As a thermoplastic material, it can be made in three different ways. It depends how the cross-linking of the polymer chains is being made. Since it is very flexible, it can be led around structures without fittings. It is the ideal material for both, hot and cold water installations.

Made from butylene that is derived from fossil fuels, thermoplastic polymer is widely used for hot and cold water installations.

Polyethylene of Raised Temperature Resistance expands the traditional properties of polyethylene. The resistance to low or high temperature makes it the ideal for a broad range of hot and cold water applications.

Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene is a thermoplastic material. This kind of pipe is mostly used for industrial applications of high impact - strength and rigidity are both essential.

CE Marking is a certification mark which indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards, for products sold across the world. However, these products have been either manufactured or designed in European Economic Area (EEA)

There are European Standards for pipes, wherein the standards are prepared with the help of CEN/TC 155. The standardisation is then followed by the committees in both, India and Europe.

In the buried pipes design, five objectives have been defined: Several data sets to become available for validating current and future design methods One clear design and installation advice to customers Avoid overkill in installation requirements Design to be in balance with feasible installation methods Increase the confidence in thermoplastics pipes for buried application in the marketplace



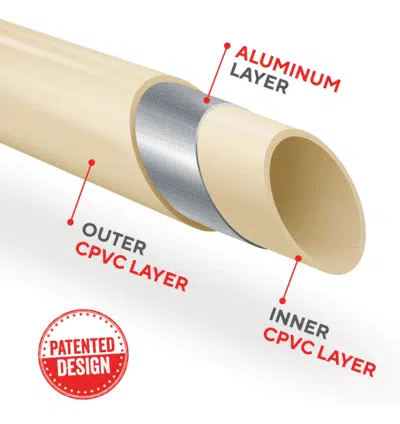



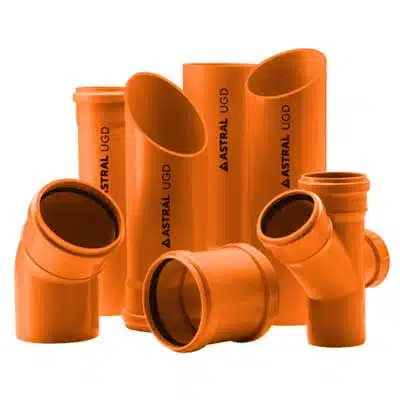
 Sewerage Drainage Pipes & Fittings
Sewerage Drainage Pipes & Fittings









 Agriculture Pipes & Fittings
Agriculture Pipes & Fittings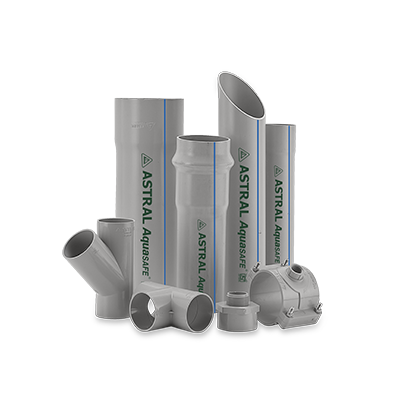
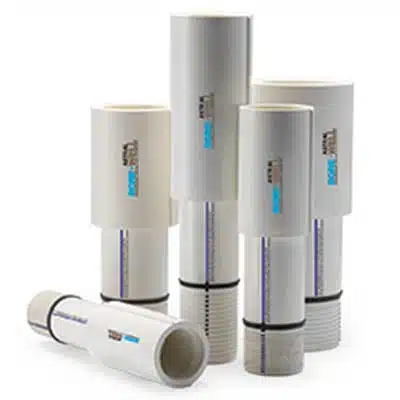
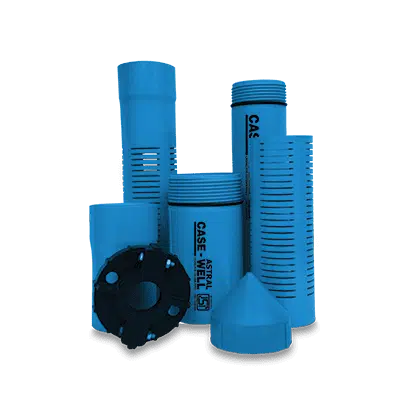




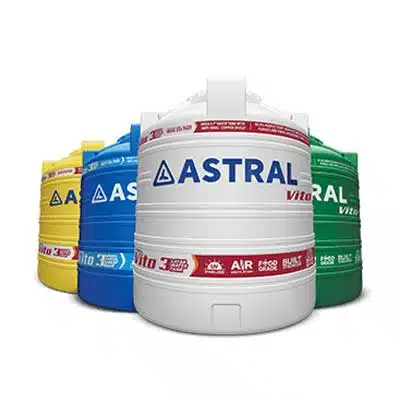
 Water Tanks
Water Tanks





 Industrial Pipes & Fittings
Industrial Pipes & Fittings




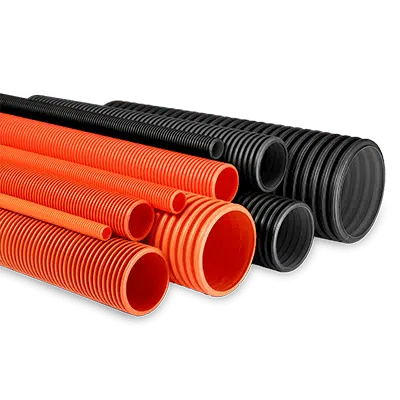
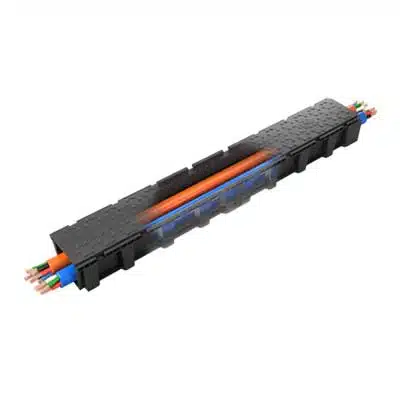
 Cable Protection
Cable Protection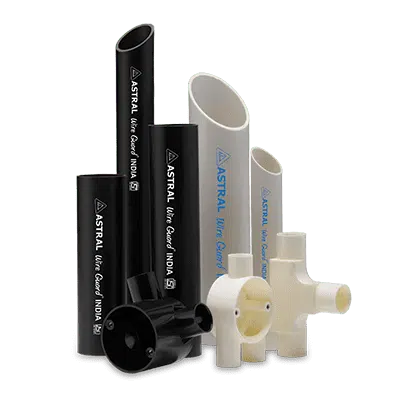


 Fire Sprinklers Pipes & Fittings
Fire Sprinklers Pipes & Fittings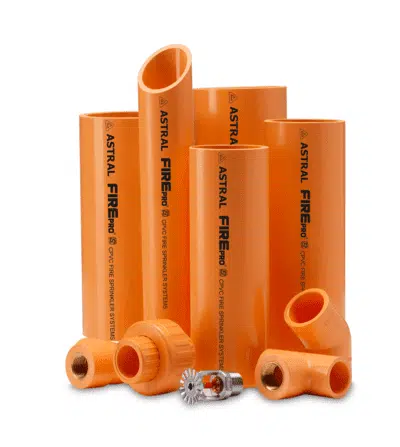
 Urban Infrastructure
Urban Infrastructure

 Ancillary Products
Ancillary Products
 Solvent Cement
Solvent Cement

 Insulation Tube
Insulation Tube
 Specialty Fittings
Specialty Fittings





